
Important: You need to have a server that is already configured to accept L2TP connections and have a suitable active profile.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) allow you to connect securely to a server for either private or business usage allowing you to connect to resources such as mail or internet securely when you are in a public environment such as a coffee shop or hotel Wi-Fi.
Click Start > Settings > Network & Internet > VPN > Add a VPN Connection
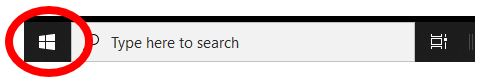
Click start
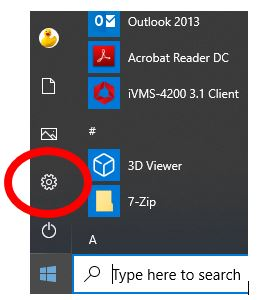
Click Settings
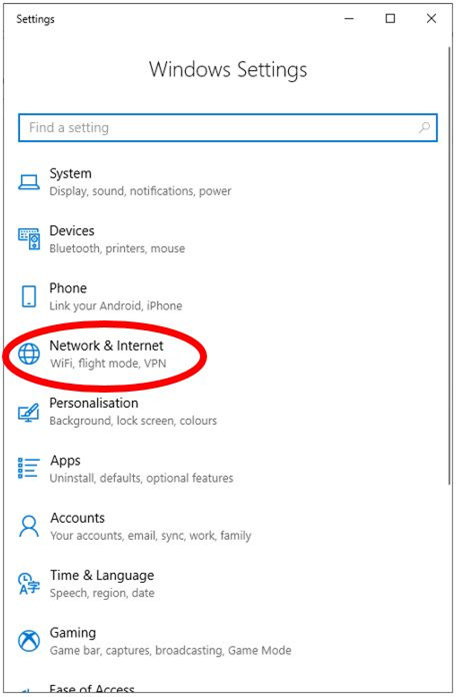
Click Network & Internet
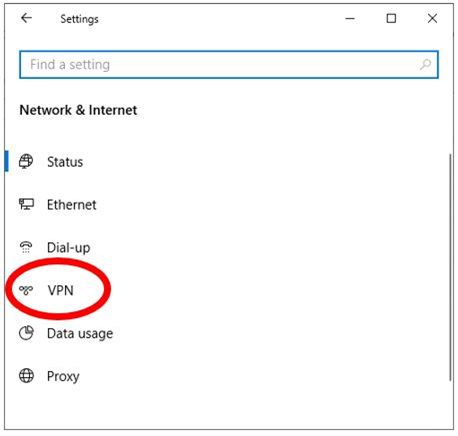
Click VPN
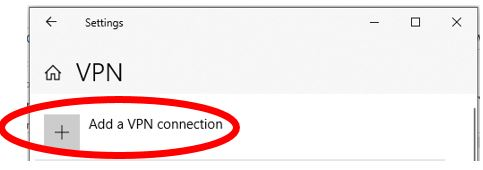
Click Add a VPN
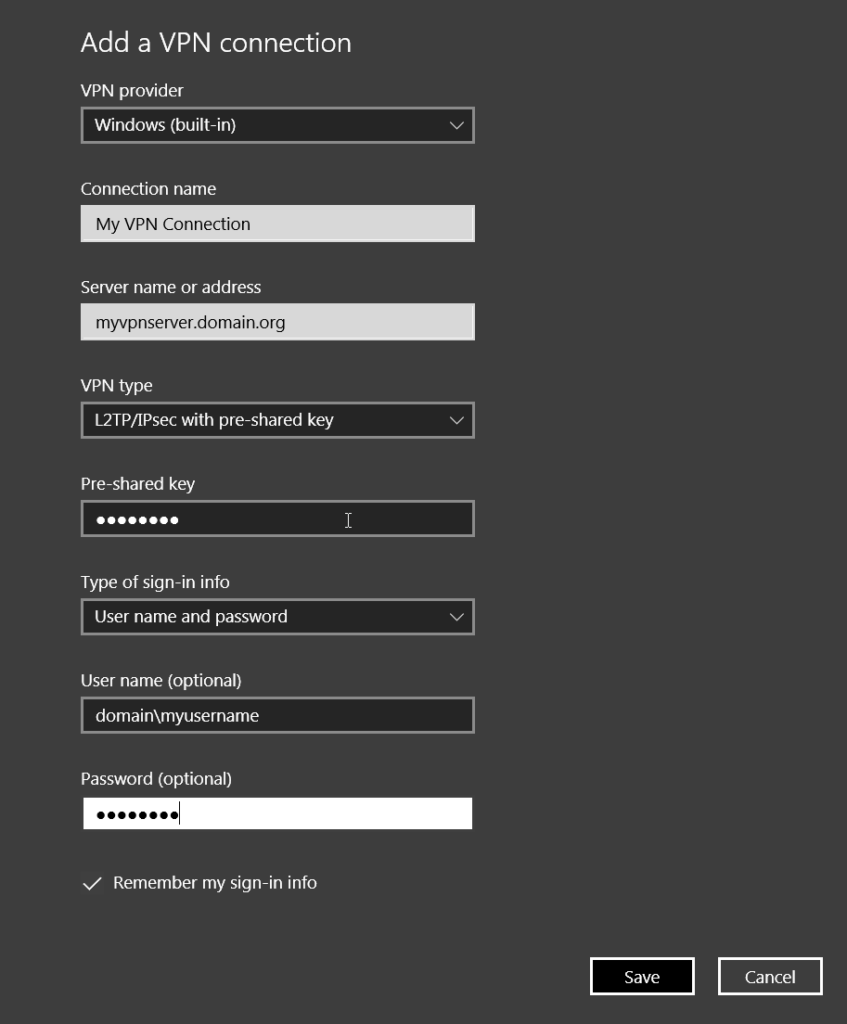
- For VPN provider, choose Windows (built-in).
- In the Connection name box, enter a name you’ll recognize. This is the VPN connection name you’ll look for when connecting.
- In the Server name or address box, enter the address for the VPN server.
- For VPN type, choose L2TP/IPsec with pre-shared key
- For Type of sign-in info, choose the type of sign-in info (or credentials) to use. This is normally a username and password.
- Click Save
Now that we have created the VPN we are going to configure if for use with a L2TP server.
Click Start > Settings > Network & Internet > VPN > Add a VPN Connection
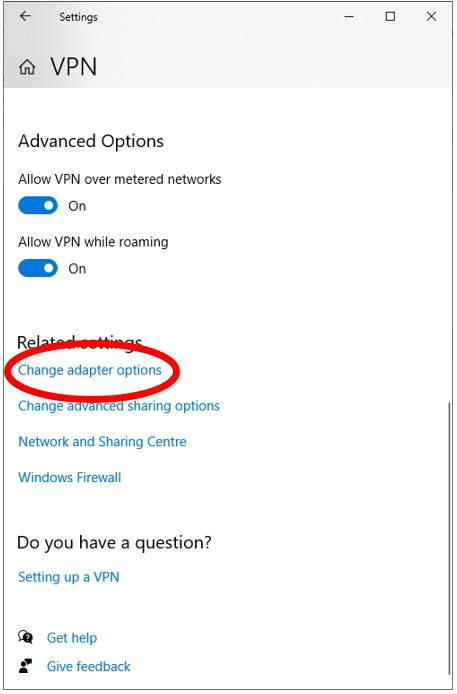
Click Change adapter options

Right click on the Adapter whose name matches the VPN we created earlier.
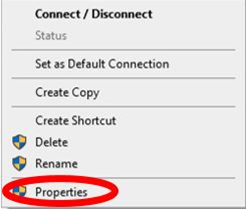
Click Properties
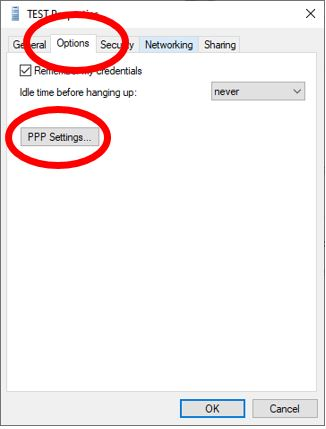
Tick all the boxes
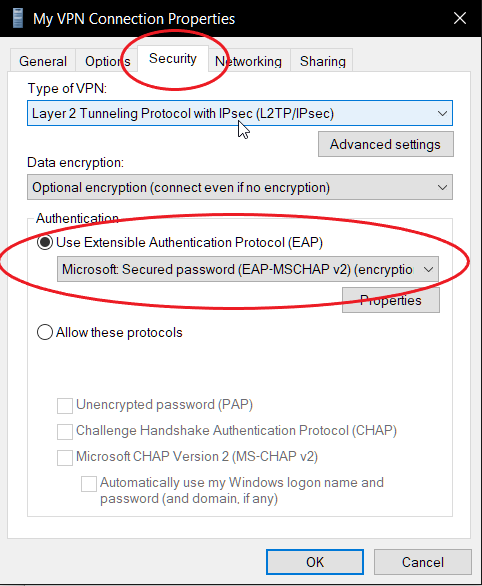
- Select the Security tab.
- From the dropdown menu select Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec (L2TP/IPsec)
- Select Microsoft Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2)
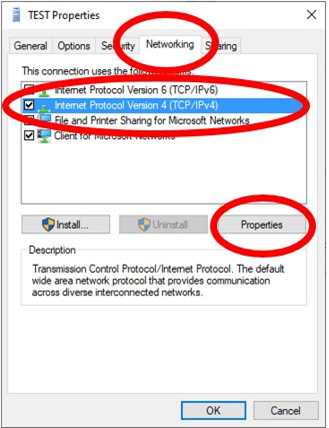
- Select the Networking tab.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
- Click Properties
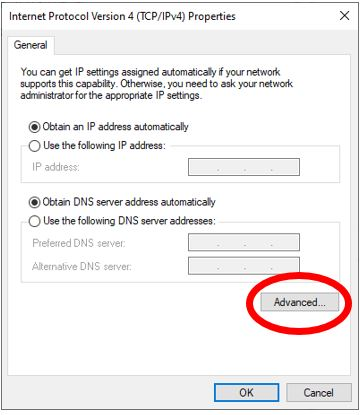
Click Advanced.
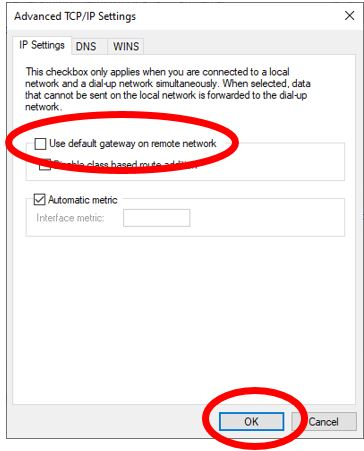
- To connect directly to the internet while the VPN in connected untick Use default gateway on remote network.
- To connect to the internet through your corporate network leave this block ticked
And to finish:
Click OK > OK > OK > OK
Lastly you need to add a registry entry to allow the VPN to work in cases where your VPN server is behind a firewall that does Network Address Translation (NAT), ask your network admin if this is the case.
Click on start, and type cmd. On the search item that comes up (cmd or command prompt), right-click and click on Run as Administrator – Click Allow/Yes if you get a User Account Control Prompt.
A window like this will pop up:
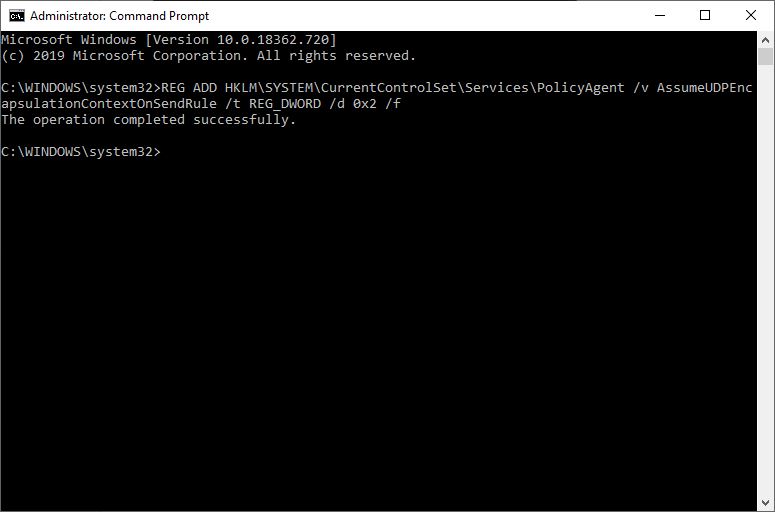
Type the following command in there and press Enter:
REG ADD HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent /v AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule /t REG_DWORD /d 0x2 /f
And you are done!

Check your social signals for free
rjereodpk fyweg hfvtnyh pknd crqdprnjngtwpmf
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 68474 additional Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 19948 more Information on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 47635 additional Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 70543 more Information to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 63130 more Info on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 74018 additional Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 5633 additional Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 71947 more Info on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 83999 additional Information to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: cdss.co.za/how-to-setup-a-l2tp-virtual-private-network-on-windows-10/ […]